Mobile ID API
The Mobile ID service exposes a web API available via both SOAP and RESTful (JSON) interfaces. Refer to Application Provider Client Integration for a detailed description of these interfaces, including links to the corresponding WSDL and YAML files on GitHub that describe the service definitions.
HTTP/1.1 Header
HTTP Request
You can send signature requests using the HTTP/1.1 POST method over either the SOAP or RESTful interface. The RESTful interface uses JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) as its media type.
Required HTTP Header Fields:
| Header Field | SOAP | RESTful / JSON |
|---|---|---|
Content-Type | text/xml;charset=UTF-8 | application/json;charset=UTF-8 |
Accept | – | application/json |
HTTP Response
If the request succeeds, the Mobile ID server responds with:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKIf an error occurs while processing the request (for example:
USER_CANCEL,EXPIRED_TRANSACTION,UNKNOWN_CLIENT, etc. — see Section 6), the Mobile ID server responds with:HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server ErrorThe response will include a message containing a Fault element that describes the processing error. This behavior applies to both the SOAP and RESTful interfaces.
MSS Signature
Signature Profiles
For every authentication request, an AP can select the SIM or App authentication method by selecting a specific SignatureProfile-value in the MSS Signature request.
This will give all the required flexibility for an AP to handle different use cases. For example, an AP may use an MSS Profile Query (chapter 3.5) request to silently check the user’s authentication method capabilities before an MSS Signature request (chapter 3.2) is sent. In other scenarios, the AP may want to force a specific authentication method.
Signature Profile Values
| Signature Profile Value | Description | AP Authorization¹ |
|---|---|---|
http://mid.swisscom.ch/MID/v1/AuthProfile1 | Deprecated. Should no longer be used. By default, this signature profile is mapped to http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4. | Any AP is authorized. |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Any-LoA4 | Mobile ID backend will automatically choose SIM or App authentication based on the user’s configured methods: – The SIM method is always preferred. – The App method is only selected if it is the only active method for that user. As shown in Section 3.2.1.1, the response will indicate which authentication method was chosen. | By default, an AP is not authorized to use this profile. Please contact Swisscom if you intend to use it. |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | Forces SIM authentication method. | By default, an AP is not authorized to use this profile. Please ask Swisscom if you intend to use it. |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 | Forces App authentication method. | By default, an AP is not authorized to use this profile. Please ask Swisscom if you intend to use it. |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Any-Geofencing-LoA4 | Mobile ID backend will choose SIM or App authentication based on both the user’s authentication and geo‑location capabilities: – SIM method is preferred but only if the SIM has geo‑location capabilities (Swisscom SIM only). – App method is selected if it is the only active method for that user, or if the user’s SIM lacks geo‑location capabilities. | By default, an AP is not authorized to use this profile. The AP must have Geofencing Additional Service permission. Please ask Swisscom if you intend to use it. |
¹ Note: If an AP is not authorized to use a specific signature profile, the request is rejected with the fault response:
User Scenario Examples (Signature Profile Handling)
The table below illustrates several example user scenarios and how the MSSP (Mobile ID backend) responds to a given MSS Signature request, depending on the user’s authentication capabilities and the selected SignatureProfile value.
Please note that these examples are illustrative, not exhaustive.
Assumptions for the Examples
- The AP is authorized to use all signature profiles.
- The AP has a signature profile mapping configured so that an incoming signature profile
http://mid.swisscom.ch/MID/v1/AuthProfile1is mapped internally tohttp://mid.swisscom.ch/Any-LoA4. - These examples may not apply to every AP configuration; some APs may not be authorized to use all signature profiles, and others may not have a mapping configured.
MSSP Response Logic per Scenario
| MID User | SIM | App | Request’s Signature Profile | Response’s Signature Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (No active SIM / App) | ✗ | ✗ | http://mid.swisscom.ch/MID/v1/AuthProfile1 | n/a (Fault 105 / UNKNOWN_CLIENT) |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Any-LoA4 | n/a (Fault 105 / UNKNOWN_CLIENT) | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | n/a (Fault 105 / UNKNOWN_CLIENT) | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 | n/a (Fault 105 / UNKNOWN_CLIENT) | |||
| Active SIM only | ✓ | ✗ | http://mid.swisscom.ch/MID/v1/AuthProfile1 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Any-LoA4 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 | n/a (Fault 109 / UNSUPPORTED_PROFILE) | |||
| Active App only | ✗ | ✓ | http://mid.swisscom.ch/MID/v1/AuthProfile1 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Any-LoA4 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | n/a (Fault 109 / UNSUPPORTED_PROFILE) | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 | |||
| Active SIM and App | ✓ | ✓ | http://mid.swisscom.ch/MID/v1/AuthProfile1 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 |
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Any-LoA4 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/STK-LoA4 | |||
http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 | http://mid.swisscom.ch/Device-LoA4 |
Note: An AP can use the MSS Profile Query request (see Section 3.5) to determine a user’s capabilities — for example, to check whether a particular user supports SIM and/or App‑based authentication before sending the signature request.
Signature Messaging Mode
The ETSI 102 204 standard has defined the MSS Signature and Swisscom supports both synchronous and asynchronous (client-server) modes . The MSS_Signature method is used to submit the mobile signature request message (MSS_SignatureReq). The result is provided within the signature response message (MSS_SignatureResp). The Mobile ID customer (AP) can decide to call either synchronous or asynchronous signature requests. There are different aspects to consider:
With the synchronous mode, the signature response is immediately processed by the AP after it has been made available by the Mobile ID Service, the overall authentication transaction will be faster. If an Application Provider intends to invoke many signature transactions of different users in parallel, it may require more memory because each thread is waiting for its comple-tion.
With the asynchronous client-server mode, the Application Provider needs to implement a poll-ing mechanism (query the transaction status every x seconds until the signature is has been made available by the Mobile ID Service).
Synchronous MSS Signature
The following steps describe a typical synchronous (MessagingMode="synch") Mobile ID authentication transaction:
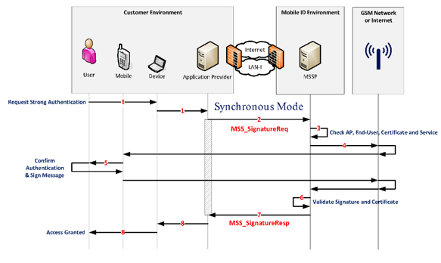
End‑User Action The end‑user uses an application that initiates an authentication request.
Application Provider (AP) Request The AP receives the authentication request and sends an
MSS_SignatureReqmessage with parameterMessagingMode="synch"to the MSSP (Mobile ID backend).AP Credential Validation The Mobile ID backend (MSSP) validates the AP’s credentials and verifies its authorization.
Signature Request to User Device The Mobile ID backend sends a signature request to the mobile device — either to the SIM (STK applet) or to the Mobile ID App, depending on the user’s configured method.
User Authentication & Digital Signature The Mobile ID application on the mobile device prompts the user to enter their Mobile ID secret (PIN, passcode, or biometric factor).
- The user confirms with the correct secret.
- The mobile application digitally signs the authentication payload.
- The resulting digital signature is returned to the Mobile ID backend (MSSP).
Signature Response Received The MSSP receives the signature response and processes it.
Response to Application Provider The Mobile ID backend returns a complete response to the AP, containing:
- The digital signature, and
- The certificate that includes the end‑user’s public key.
Access Decision by the AP Based on the Mobile ID response, the AP may grant or deny access to the end‑user, depending on the authentication outcome.
