Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide technical documentation and guidelines on how to use the Swisscom Mobile ID Authentication API.
The Swisscom Mobile ID authentication solution protects access to your company data and applications with a comprehensive end‑to‑end solution for two‑factor authentication (2FA). Mobile ID can be used in multiple processes — from simple two‑factor login to password‑free authentication, online signatures, and geofencing. It is suitable for various system landscapes and meets strict regulatory requirements.
➡️ For more information, visit https://mobileid.ch.
Terms and Abbreviations
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| AP | Application Provider |
| AP_ID | Application Provider Identifier |
| DTBD | Data‑To‑Be‑Displayed — message displayed on the mobile phone (authentication context). |
| DTBS | Data‑To‑Be‑Signed — equal to DTBD; the data that will be signed with the Mobile ID signing key. |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation — text‑based open standard data interchange format. |
| LAN‑I | Swisscom LAN‑Interconnect Service (Enterprise WAN). |
| MID | Mobile ID platform providing the mobile signature service. |
| MNO | Mobile Network Operator — also called wireless service provider or carrier. |
| MSISDN | Number uniquely identifying a mobile subscription in a GSM/UMTS network. |
| MSSP | Mobile Signature Service Provider — Swisscom Mobile ID backend application. |
| OTA | Over‑The‑Air management technology for SIM communication. |
| RESTful | Style of software architecture for distributed systems relying on HTTP. |
| SOAP | Simple Object Access Protocol — XML‑based exchange protocol. |
| WSDL | Web Services Description Language — XML‑based web‑service contract description. |
| X509 | Public‑Key Infrastructure and digital certificates standard. |
| XML | Extensible Markup Language — structured, human‑ and machine‑readable document format. |
Mobile ID Signature Service (MSS)
Mobile ID is a cost‑efficient, managed authentication service operated by Swisscom. The customer‑facing API follows the open standard ETSI 102 204 V1.1.4 (2003‑08).
Authentication in Mobile ID is based on a secure hardware token which can be either:
- a Mobile ID‑compliant SIM or eSIM, or
- a Mobile ID App running on a smartphone.
Therefore, a user account could have either the (e)SIM method, the App method or even both methods activated at the same time. However, the Application Provider (AP) may select the preferred method and allow both methods or just either one.
Mobile ID SIM - Method
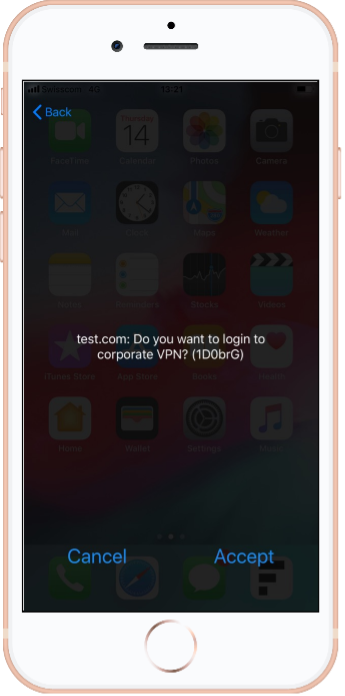
An Application Provider (AP) can request SIM Toolkit (STK) based authentication, hereinafter referred as "SIM method". To utilize the SIM method, the user must have a Mobile ID compliant SIM card or eSIM. Data exchange between the Mobile ID server and the STK application is done with SMS messages using data packets (PDUs), not visible to the end-user. The Mobile ID SIM Toolkit application runs on the SIM card environment and is compliant with all mobile devices.
Key Advantages
Strong Two‑Factor Authentication
- 1st Factor: Physical SIM/eSIM (Possession Factor)
- 2nd Factor: Personal Mobile ID PIN (Knowledge Factor)
High Level of Security
- Tamper‑proof secure hardware (EAL5+ and ITSEC E3 certified)
- Authentication via a separate encrypted channel
Pre‑installed STK App on the SIM/eSIM profile
Supported by most Swiss Mobile Network Operators (Swisscom, Sunrise, Salt)
Mobile ID App - Method
An Application Provider (AP) can request mobile app based authentication, hereinafter referred as "App method". To utilize the App method, the user must have the Mobile ID App installed on a compliant Android or iOS-based smartphone. The app can be downloaded from Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
Activation Options
The Mobile ID App activation can be done within the mobile app (in-app enrolment) or through the selfcare portal (in latter case, the app must scan a QR code displayed on www.mobileid.ch).
In‑App Enrolment The user activates Mobile ID directly within the app.
Self‑Care Portal Activation Activation via https://www.mobileid.ch, where the app scans a QR code displayed on the site.
Display Options
The App can display a plain UTF-8 string as a single text line. This is known as the DTBD (DataToBeDisplayed) Classic View.
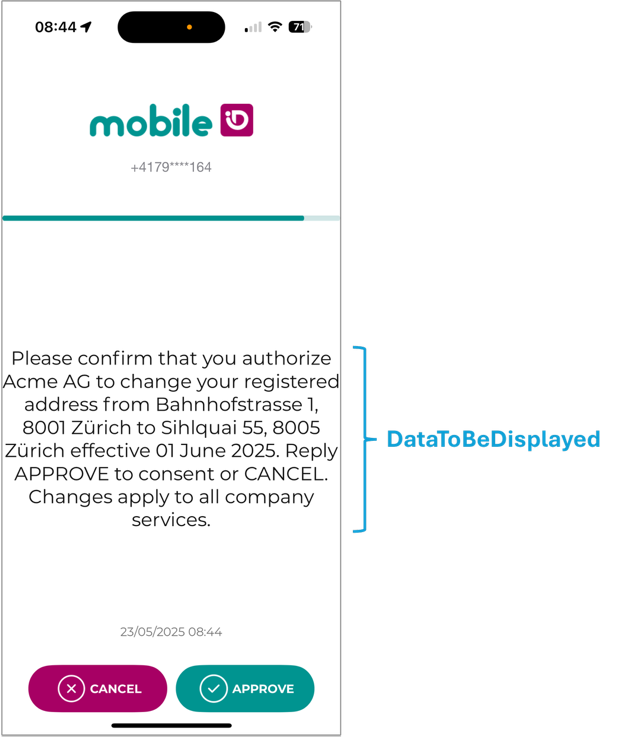
The App also supports Transaction Approval Style, which enhances readability by displaying a title (type-field) and one or more key-value rows.

App Method Key Advantages
Strong Two-Factor Authentication
- 1st Factor: Smartphone (Possession Factor)
- 2nd Factor: Passcode (Knowledge Factor) or Biometry (Inherence Factor)
High Level of Security
- Authentication through dedicated mobile application (authentication app)
- Fast and secure (encrypted) communication
Availability
- The app is published and available in several countries of the European Union (EU)
Authentication Flow
Before going into more technical details, let’s have a short look at the main scenario.
Strong Authentication: The end-user wants to access a corporate application protected by Mobile ID strong authentication.
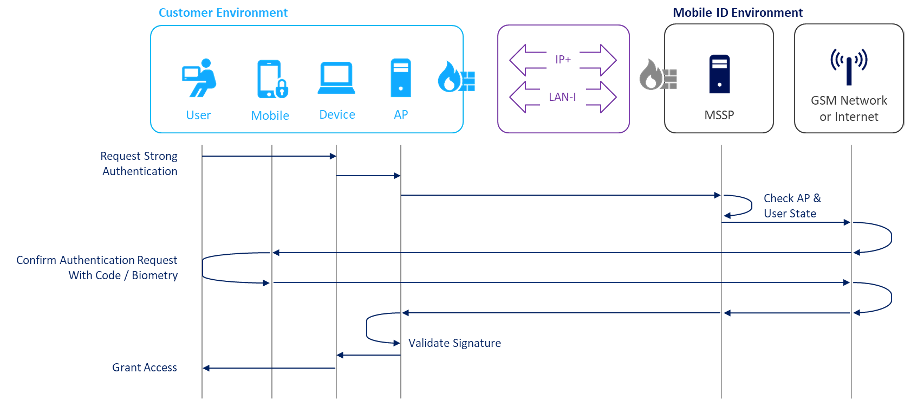
Main Steps Performed by the End-User and the Mobile Signature Service
The end-user uses any application relying on Mobile ID for authentication.
- The application sends a mobile signature request through the dedicated web interface (of the AP), including the personal MSISDN as an input parameter to log in.
The AP receives the end-user request, forms the contents to be signed (in accordance with the ETSI TS 102 204 standard), and forwards the request to the MID service.
The MID platform receives the signature request and validates the AP in accordance with the service agreement.
The MID platform ensures that the end-user signature request is allowed and forwards the signature request to the end-user’s mobile phone.
The end-user receives a message on their mobile phone to sign the mobile signature request.
- The end-user confirms the authentication request either by providing the Mobile ID PIN (SIM method) or Passcode/Biometry (App method).
After the AP has received a valid response, the end-user is granted access to the corporate application.
